Understanding How Holes Form in Teeth
A cavity, also known as tooth decay, can indeed cause a hole in the tooth. When plaque and bacteria build up on the surface of the teeth, they produce acids that gradually erode the enamel, leading to small holes or cavities. These cavities can worsen over time if left untreated, causing pain and discomfort. In this article, we will explore the causes of cavities and their impact on dental health.
Tooth decay is a common oral health issue that affects people of all ages. It occurs when bacteria in our mouths feed on sugars from food and drinks to produce acids. Over time, these acids attack the outer layer of our teeth called enamel, weakening it and forming tiny holes or cavities.
If not addressed promptly with proper dental care and hygiene practices such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups; cavities can progress deeper into the tooth structure. This can lead to more extensive damage like infections or abscesses which may require more invasive treatments such as root canal therapy or even extraction.
Understanding how cavities develop is crucial for maintaining good oral hygiene habits and preventing future dental problems. In this article, we will delve into the various factors contributing to cavity formation while exploring effective preventive measures you can take to keep your pearly whites healthy and hole-free! So let’s jump right in!
What is a Cavity?
- A cavity, also known as tooth decay or dental caries, is a common dental problem that occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the hard tissues of the teeth.
- It begins with the formation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the surface of teeth. Plaque can build up if not removed by proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing.
- When plaque interacts with sugars and starches from food, it produces acid that attacks tooth enamel – the protective outer layer of the tooth. Over time, this acid attack can weaken and break down enamel, leading to cavities.
- Initially, cavities may appear as small white spots on the affected teeth. As they progress, they form holes or pits in the tooth structure.
- Cavities can occur in various parts of a tooth:
- Pit and fissure cavities develop in grooves on chewing surfaces where plaque accumulates easily.
- Smooth surface cavities form on flat areas between teeth or along gumlines.
- Root cavities occur on exposed root surfaces when gums recede due to aging or gum disease.
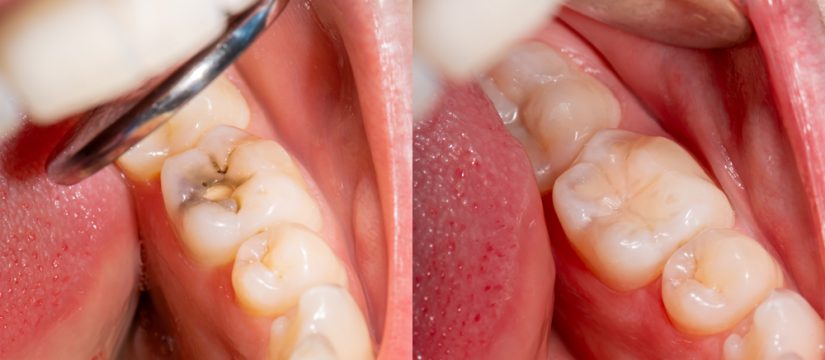
Cavities are more likely to develop under certain conditions:
-
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque buildup and increase cavity risk.
-
Sugary Diet: Frequent consumption of sugary foods and drinks provides fuel for bacteria to produce harmful acids.
-
Acidic Foods/Drinks: Regular exposure to acidic substances like citrus fruits or sodas weakens enamel’s resistance against cavity-causing acids.
-
Dry Mouth: Reduced saliva flow due to medical conditions or medications contributes to cavity formation.
-
Tooth Anatomy: Deep crevices or tight spaces between teeth make cleaning difficult, increasing susceptibility to decay.
-
Lack of Fluoride: Insufficient fluoride intake or lack of exposure to fluoridated water and dental products can weaken enamel’s ability to resist cavities.
It is important to maintain good oral hygiene practices, limit sugary foods/drinks, and visit the dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings to prevent or address cavities promptly.
Common Causes of Cavities
Cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are a common oral health problem affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes of cavities is essential for maintaining good oral hygiene and preventing tooth damage. Here are some common causes of cavities:
-
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up on teeth. Plaque contains harmful bacteria that produce acids, leading to enamel erosion and cavity formation.
-
High Sugar Consumption: Consuming sugary foods and drinks frequently can significantly increase the risk of developing cavities. Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugar, producing acid as a byproduct that attacks tooth enamel.
-
Frequent Snacking: Snacking throughout the day without proper oral hygiene practices doesn’t give your saliva enough time to neutralize acids produced by bacteria after eating. This prolonged exposure increases cavity risk.
-
Lack of Fluoride: Fluoride is crucial for strengthening tooth enamel and protecting against acid attacks from bacteria in plaque. Insufficient fluoride intake or lack of exposure to fluoridated water can increase cavity susceptibility.
-
Dry Mouth: Saliva plays an important role in maintaining oral health by washing away food particles and neutralizing acids produced by bacteria in plaque. A dry mouth condition reduces saliva production, making it easier for cavities to develop.
-
Deep Tooth Crevices: Deep grooves or fissures on the chewing surfaces of teeth can provide hiding places for food particles and bacteria, increasing the likelihood of cavities forming over time if not properly cleaned.
7** .** Acidic Foods and Drinks:** Frequent consumption of acidic foods like citrus fruits, soda, sports drinks, or carbonated beverages can lead to enamel erosion over time due to their corrosive nature.
By understanding these common causes , you can take proactive steps towards preventing cavities and maintaining good oral health. Regular brushing, flossing, limiting sugar intake, and visiting your dentist for check-ups are essential for cavity prevention.
Poor Oral Hygiene and Cavities
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial in preventing cavities. When proper dental care practices are not followed, the risk of developing tooth decay increases significantly. Here are some key points to understand the relationship between poor oral hygiene and cavities:
-
Inadequate Brushing: Failing to brush your teeth thoroughly and regularly allows plaque to accumulate on the tooth surfaces. Plaque is a sticky film made up of bacteria that produce acids when exposed to sugars from food and drinks. These acids attack the enamel, causing it to weaken over time.
-
Insufficient Flossing: Neglecting flossing means leaving behind harmful bacteria and food particles trapped between your teeth where a toothbrush can’t reach easily. This leads to an increased risk of cavities forming in these hard-to-reach areas.
-
Lack of Regular Dental Check-ups: Skipping routine dental check-ups prevents early detection and treatment of any potential oral health issues, including cavities. Dentists can identify early signs of decay or weak spots in enamel through X-rays or visual examination before they progress into more significant problems.
-
Unhealthy Dietary Habits: Consuming sugary foods, snacks, and beverages frequently throughout the day creates a constant supply of sugar for bacteria in your mouth, leading to higher acid production that erodes tooth enamel faster.
-
Dry Mouth Syndrome: Insufficient saliva flow due to certain medications or medical conditions can increase cavity formation risks since saliva helps wash away food particles and neutralize acid produced by bacteria.
To maintain good oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste.
- Use dental floss once a day.
- Schedule regular visits with your dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks intake.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
By prioritizing proper oral hygiene practices, you can significantly reduce the chances of developing cavities and maintain a healthy smile.
Sugar Consumption and Dental Decay
Excessive sugar consumption is a major factor in the development of dental cavities. When you consume sugary foods and drinks, the bacteria present in your mouth feed on these sugars and produce acids as byproducts. These acids attack the tooth enamel, which is the protective outer layer of your teeth, leading to tooth decay over time.
Here are some important points to consider regarding sugar consumption and dental decay:
-
Frequency: The frequency at which you consume sugary foods or drinks plays a significant role in cavity formation. Each time you have something sweet, it takes about 20 minutes for your saliva to neutralize the acid produced by bacteria. Therefore, frequent snacking or sipping on sugary beverages prolongs this acid attack period and increases the risk of developing cavities.
-
Amount: The amount of sugar consumed also impacts dental health. Foods with high levels of added sugars like candy, soda, cookies, and cakes can contribute significantly to tooth decay if consumed excessively.
-
Sticky Sugars: Sticky candies or snacks that cling to your teeth for longer periods expose them to prolonged acid attacks, increasing the likelihood of cavities forming.
-
Hidden Sources: Many processed foods contain hidden sugars that may not be immediately obvious from their taste but can still contribute to dental decay over time. Examples include flavored yogurt, cereal bars, sauces, salad dressings, and even some bread products.
To reduce the risk of developing cavities due to sugar consumption:
- Limit intake: Reduce overall sugar intake by making conscious choices about what you eat and drink.
- Choose healthier alternatives: Opt for fresh fruits instead of sweets or choose water or unsweetened beverages over sugary drinks.
- Practice good oral hygiene: Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste helps remove plaque buildup caused by bacterial activity.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visiting your dentist regularly allows early detection of any dental issues and enables prompt treatment.
By being mindful of your sugar consumption and maintaining good oral hygiene practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of cavities and maintain a healthy smile.
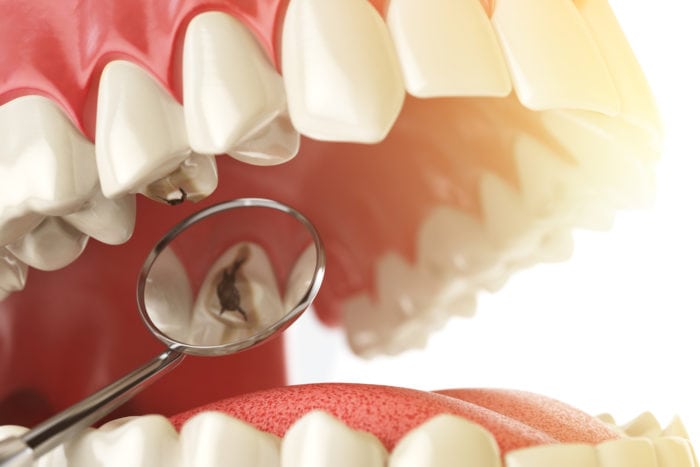
Acidic Foods and Tooth Erosion
Tooth erosion occurs when the tooth enamel is worn away by acids. One of the main causes of tooth erosion is consuming acidic foods and beverages on a regular basis. Here are some important points to consider:
-
Foods and Beverages High in Acidity: Certain foods and drinks have high acid content, which can contribute to tooth erosion. Some examples include citrus fruits (lemons, oranges), tomatoes, pickles, vinegar-based dressings, carbonated sodas, fruit juices (especially those with added sugars), energy drinks, and wine.
-
pH Levels: The pH scale measures acidity levels in substances from 0 to 14. A pH below 7 indicates acidity. When it comes to oral health, lower pH values can be harmful as they increase the risk of tooth erosion.
-
Effects on Enamel: Acidic foods weaken the protective enamel layer that covers your teeth. Over time, this leads to demineralization—the loss of minerals such as calcium and phosphate—which makes teeth more susceptible to cavities.
-
Frequency Matters: It’s not just about what you eat or drink; how often you consume acidic substances also plays a role in tooth erosion. Frequent exposure prolongs contact between acids and teeth, increasing the chances of damage.
-
Protective Measures: While it may be challenging to eliminate all acidic foods from your diet entirely—some are nutritious after all—you can take steps to minimize their impact:
- Consume acidic food or drinks during meals rather than as snacks.
- Rinse your mouth with water after consuming an acidic substance.
- Wait at least 30 minutes before brushing your teeth after eating or drinking something highly acidic.
- Use a straw when drinking acidic beverages to reduce direct contact with teeth.
6 .Regular Dental Care: Maintain good oral hygiene habits such as brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups. These practices can help protect your teeth from erosion caused by acidic foods.
Remember, moderation is key when it comes to consuming acidic foods and beverages. By being mindful of the impact they can have on your oral health and taking preventative measures, you can minimize the risk of tooth erosion and maintain a healthy smile.
Genetic Factors in Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is a common oral health issue that can be influenced by genetic factors. While proper oral hygiene and dietary habits play a significant role in preventing tooth decay, genetics can contribute to an individual’s susceptibility to this condition. Here are some key points regarding the impact of genetic factors on tooth decay:
-
Saliva Composition: The composition of saliva is partially determined by our genes, and certain variations can affect its ability to protect against tooth decay. Saliva helps neutralize acids produced by bacteria and remineralize teeth after acid attacks.
-
Enamel Strength: Enamel acts as a protective barrier for our teeth, and its strength is partly influenced by genetic factors. Variations in genes responsible for enamel formation may result in weaker enamel that is more prone to demineralization and cavity development.
-
Taste Preferences: Our taste preferences are influenced by genetics, including the preference for sugary foods and beverages that can lead to tooth decay if consumed excessively.
-
Immune Response: Genetic variations can impact an individual’s immune response to bacterial infections in the mouth, such as Streptococcus mutans, which plays a crucial role in initiating tooth decay.
-
Salivary pH Levels: Differences in salivary pH levels among individuals could be attributed to genetic factors. Lower pH levels indicate increased acidity, creating an environment favorable for bacterial growth and subsequent cavity formation.
While it’s important to note that genetics alone do not determine whether someone will develop cavities or not; they do contribute alongside other lifestyle and environmental factors like diet choices, oral hygiene practices, fluoride exposure, etc.
Understanding the role of genetic factors provides valuable insights into personalized preventive strategies against tooth decay tailored towards individuals with higher susceptibility due to their unique genetic makeup.
Preventing Cavities: Tips and Tricks
Cavities can be painful and costly to treat. By following these simple tips and tricks, you can help prevent cavities and maintain a healthy smile:
- Brush regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Use small circular motions and ensure that you clean all surfaces of your teeth.
- Floss daily: Flossing helps remove plaque from between your teeth where the toothbrush cannot reach. Make it a habit to floss every day to keep your gums healthy.
sugary foods and drinks: Sugary snacks and beverages provide food for harmful bacteria in the mouth, leading to cavity formation. Reduce consumption of candies, sodas, juices, and other sugary treats.
- Choose water over soda: Water is not only hydrating but also helps wash away food particles from your teeth. Opt for water instead of sugary or acidic drinks whenever possible.
-
Use fluoride products: Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay. Look for fluoride toothpaste, mouthwash, or dental treatments recommended by professionals.
-
Visit the dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups are crucial in preventing cavities as dentists can identify early signs of decay or other oral health issues before they worsen.
-
Consider dental sealants: Dental sealants are thin protective coatings applied on the chewing surfaces of back teeth (molars). They create a barrier against cavity-causing bacteria.
Remember that prevention is key when it comes to maintaining good oral health! By implementing these tips into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing cavities and enjoy a healthier smile for years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cavities are a common dental issue that can cause holes in teeth. These holes are the result of decay caused by bacteria and plaque buildup on the tooth’s surface. It is important to understand the causes of cavities in order to prevent them and maintain good oral health.
By practicing regular brushing and flossing, as well as visiting the dentist for check-ups, individuals can minimize their risk of developing cavities. Additionally, adopting a healthy diet low in sugary foods and drinks can also help prevent cavity formation.
Early detection and treatment of cavities are crucial to avoid further damage to the tooth structure. If left untreated, cavities can lead to pain, infection, and even tooth loss. Therefore, it is essential to address any signs or symptoms promptly by seeking professional dental care.
Overall, maintaining good oral hygiene habits along with regular dental visits are key factors in preventing cavity formation and preserving the health of our teeth. By taking proactive steps towards prevention, we can ensure strong and healthy smiles for years to come.
